Your phone lights up at 3 a.m. with a notification: a coin you held has swung twenty percent overnight, and your heart races faster than the price chart. That jolt — the abrupt reality of volatility — is where most traders’ journey begins, and where strategy matters more than luck.
Across exchanges, patterns repeat: momentum runs, liquidity gaps, sentiment-driven pumps, and quiet accumulations that foreshadow big moves. Understanding trading strategies means recognising which market behavior you’re facing, not chasing every signal or treating charts like prophecy.
For traders in Nigeria and beyond, the core challenge is practical: convert structural market knowledge into repeatable decisions that respect risk, capital limits, and execution friction. This overview traces the landscape of cryptocurrency approaches, contrasts their trade-offs, and highlights where common mistakes quietly erode returns.
Risk Management and Portfolio Construction
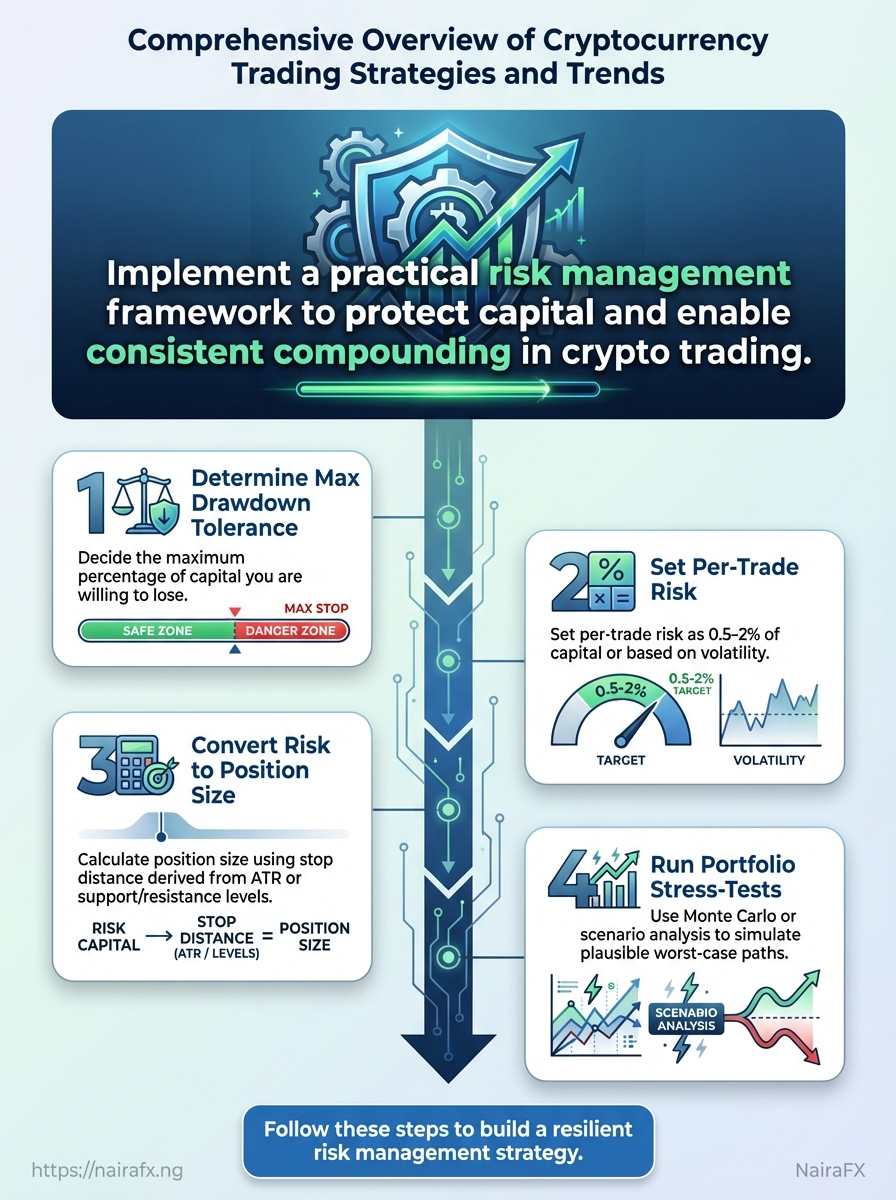
Risk controls determine whether a trading career survives market stress. Start by deciding how much capital you’re willing to risk per trade and how that scales across the portfolio. Position sizing, volatility-aware stops, and stress-testing against extreme scenarios keep drawdowns manageable and allow consistent compounding when strategies work.
Position sizing: Position size should be a function of portfolio risk, not ego. Use a fixed-percentage or volatility-adjusted rule to limit loss per trade and avoid ruin.
Volatility-adjusted stops: Use measures like ATR (Average True Range) to set stops that adapt to current market noise, reducing false stop-outs during high volatility.
Tail-risk planning: Accept that rare, large moves happen. Allocate a portion of capital to hedge or strategies that benefit from extreme moves, and avoid overconcentration in correlated risk.
How to construct a practical risk framework
- Determine maximum portfolio drawdown tolerance.
- Set per-trade risk as a percentage of capital (commonly
0.5–2%) or risk multiple based on volatility. - Convert per-trade risk into position size using stop distance derived from
ATRor support/resistance levels. - Run portfolio-level stress-tests (Monte Carlo or scenario analysis) to see plausible worst-case paths.
Practical checks and adjustments
- Diversify by risk driver: Spread exposure across uncorrelated instruments or strategies rather than only diversifying by ticker.
- Cap concentrated bets: Rule: no single position should threaten more than X% of equity (set X based on your risk profile).
- Dynamic rebalancing: Adjust sizes after large moves so risk remains aligned with targets.
Stress-testing and tools
Run Monte Carlo simulations to generate many return paths and estimate the distribution of drawdowns and recovery times. Monte Carlo highlights the likelihood of sequences that destroy expectancy even from a profitable edge.
Example — volatility-adjusted stop Measure ATR(14) = 0.8% on a currency pair. Risk per trade = 1% of portfolio. Position size = (1% of portfolio) / (0.8% number_of_units).
This keeps stop placement meaningful and position sizing consistent across regimes. Where possible, include a small portion of tail-risk hedges or option structures to blunt extreme moves; they reduce short-term performance but protect capital when it matters most.
Applying these rules reduces surprise drawdowns and preserves optionality to compound when the market offers edges again. Keep the framework simple, test it under stress, and let risk controls enforce discipline when emotions push otherwise.
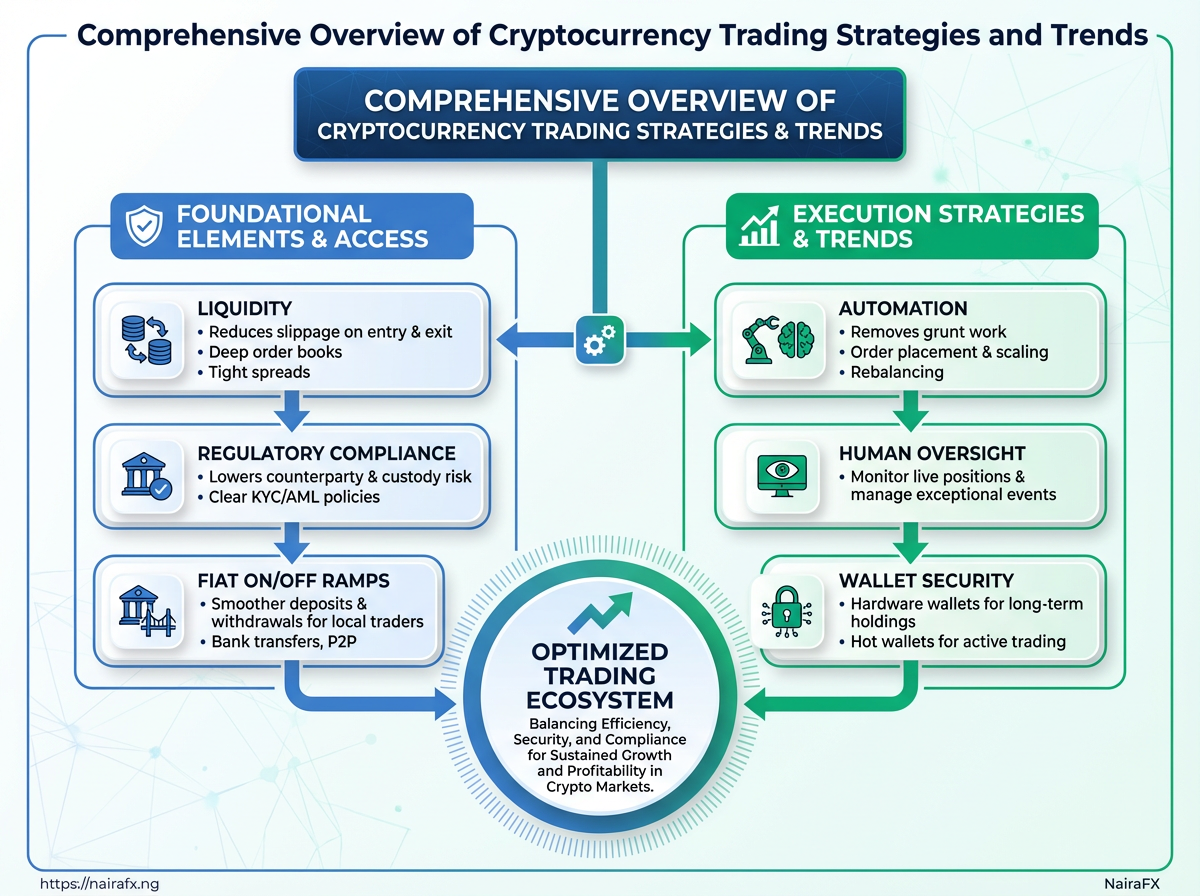
Tools, Platforms, and Execution Best Practices
Choose platforms and tools with three priorities: liquidity, regulatory compliance, and reliable fiat on/off ramps. Liquidity reduces slippage on entry and exit. Compliance lowers counterparty and custody risk. Good fiat rails mean smoother deposits and withdrawals for Nigerian traders using bank transfers, P2P, or regulated fiat gateways. Automation should remove grunt work—order placement, scaling, rebalancing—while keeping a human in the loop to monitor live positions and manage exceptional events. For long-term holdings, move sizeable balances to hardware wallets and use hot wallets only for active trading.
Liquidity: Deep order books and tight spreads reduce execution cost and slippage.
Regulatory compliance: Exchanges with clear KYC/AML policies and local payment partnerships limit operational risk.
Fiat on/off ramps: Support for Naira pairs, P2P, or integrated NGN payment providers cuts conversion friction.
Selecting exchanges, wallets, and automation tools
| Tool category | Selection criteria | Example providers | Primary use case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Centralized exchanges | High liquidity, strong security, NGN/P2P support | Binance (P2P), Coinbase (regulated), Kraken (fiat rails) | Spot, margin, futures trading with fiat rails |
| Decentralized exchanges / aggregators | On-chain liquidity, low counterparty risk, token listings | Uniswap (Ethereum), PancakeSwap (BSC), 1inch (aggregator) | Token swaps, AMM-based liquidity, arbitrage sourcing |
| Wallets (hot / hardware) | Private key control, ease of use, backup options | MetaMask (hot), Trust Wallet (hot), Ledger (hardware), Trezor (hardware) | Active trading (hot) vs long-term cold storage (hardware) |
| Trading bots / automation | Strategy templates, exchange API support, backtesting | 3Commas (cloud), Hummingbot (open-source), Zignaly (PAMM) | Execution of strategies, grid/scalping, portfolio rebalancing |
| Portfolio trackers | Multi-exchange aggregation, tax/export tools, mobile alerts | CoinStats, CoinGecko Portfolio, Delta | Performance tracking, P&L, tax reporting prep |
Key insight: The right mix combines a liquid centralized exchange for execution, DEX access for on-chain opportunities, hardware wallets for custody, automation for repeatable actions, and a portfolio tracker for oversight. Choose providers that match the trader’s time horizon and regulatory comfort.
Practical execution checklist: 1. Evaluate liquidity and fees on target pairs, then fund a small test trade. 2. Configure API keys with trade-only permissions and IP restrictions. 3. Backtest strategies and run on a paper account or sandbox before live. 4. Keep long-term holdings on hardware wallets and only expose operational capital on hot wallets. 5. Monitor automated strategies daily and pause on unusual volatility.
Use automation to reduce manual errors, but keep monitoring tight—markets change faster than bots. Consistent platform selection and execution hygiene make strategies repeatable and protect capital in volatile conditions.
Strategy Implementation: Sample Playbooks and Backtesting
Start with concise, testable playbooks: precise entry rules, clear stop-loss and position sizing, and defined exit logic. Keep each playbook short enough that a script can reproduce it without human interpretation. Backtest broadly, stress the rules across different market regimes, then forward-test small before allocating meaningful capital.
Playbook design principles
Reproducibility: Rules expressed so a backtester or developer can implement them without ambiguity. Regime awareness: Separate parameter sets for trending, mean-reverting, and high-volatility periods. Risk per trade: Fixed fraction or volatility-adjusted sizing, never ad-hoc amounts. Exit clarity: Time-based exits, profit targets, or stop-loss cascades—pick one primary exit and one fail-safe.
- Identify candidate playbook and codify rules precisely.
- Backtest across at least three market regimes using historical data (trend, range, high volatility).
- Run Monte Carlo re-samples on trade sequence to estimate distribution of outcomes.
- Forward-test with micro-sized live or paper positions for 30–90 days.
- Scale gradually if forward-test results align with backtest distributions.
Practical execution notes
- Data hygiene: Always use cleaned, adjusted price series and consistent timezone handling.
- Transaction costs: Include realistic spreads and slippage in simulations.
- Overfitting guard: Prefer fewer parameters and validate out-of-sample performance.
Template table for recording backtest results across key metrics and market regimes
| Playbook | Market regime | Win rate | Expectancy | Max drawdown | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Momentum swing | Trending (bull/bear) | 40–55% | 0.8–1.5 R | 8–20% | Works best on higher timeframes; needs trend filter |
| Scalping (low timeframe) | Low volatility, high liquidity | 55–70% | 0.05–0.2 R | 3–10% | Sensitive to latency and fees |
| Volatility breakout | High-volatility regimes | 30–45% | 1.0–2.5 R | 10–25% | Large winners offset low win rate |
| Arbitrage | Cross-exchange / fragmented markets | 85–98% | 0.01–0.1 R | 1–5% | Execution & funding risks; requires automation |
| Yield strategy | Stable, low-volatility assets | 65–90% | 0.2–0.6 R | 2–12% | Depends on funding rates and counterparty risk |
Key insight: The table frames realistic performance ranges rather than guarantees. Use these ranges to set expectations, stress-test position sizing, and prioritize liquidity and cost modeling during backtests.
This approach turns abstract ideas into recorded experiments: codify, test across regimes, check robustness with Monte Carlo, then forward-test with small size. Repeating that loop consistently separates robust strategies from curve-fitted curiosities.
Regulation, Taxes, and Operational Considerations for Nigerian Traders
Regulatory compliance, tax treatment, and reliable cash rails are not optional extras — they shape whether a trading plan survives market stress or falls apart at withdrawal time. Nigerian traders need practical routines: keep meticulous records, choose regulated on/off-ramps, and treat AML/KYC requirements as operational constraints rather than paperwork nuisances.
Compliance basics
KYC (Know Your Customer): Financial platforms require verified identity and proof of address; incomplete KYC can freeze funds.
AML (Anti-Money Laundering): Large or unusual flows trigger reviews; expect requests for proof of funds and transaction explanations.
Taxable event: Realized profits on disposals or converted gains (local interpretation may vary) usually create a tax obligation; treat trading as taxable activity and plan accordingly.
Practical steps for reporting and audits
- Maintain a consolidated trade log.
- Store timestamped order confirmations, executed fills, exchange statements, and bank receipts.
- Keep clear records of fiat on/off-ramps and wallet movements for at least five years where possible.
- Use consistent valuation method (e.g., cost basis in naira) and note exchange rates used for conversions.
Operational choices that reduce friction
- Choose regulated on-ramps: Prefer banks and licensed Nigerian forex/crypto platforms for deposits and withdrawals.
- Use documented OTC/fiat partners: When using peer-to-peer (P2P) channels, retain trade screenshots, counterparty IDs, and receipts.
- Segregate accounts: Keep trading capital separate from living funds for clearer audit trails.
Handling taxes without overcomplication
- Record realized P/L: Track every closed position’s realised profit or loss in naira.
- Document transfers: Record date, amount, and conversion rate for each fiat conversion.
- Engage a tax advisor early: An experienced Nigerian tax accountant will map trading activity into income, capital gains, or business profits depending on frequency and intent.
Operational risk controls
- Backups: Keep encrypted backups of logs and KYC documents off-site.
- Access controls: Use 2FA, hardware wallets for custody where applicable, and separate email for financial accounts.
- Stress tests: Simulate withdrawal scenarios quarterly to ensure chosen rails work under duress.
Keeping tidy records and using regulated rails turns regulatory risk into predictable processes, not surprises. That discipline prevents most headaches when taxes, audits, or withdrawal checks come knocking.
📝 Test Your Knowledge
Take this quick quiz to reinforce what you’ve learned.
Future Trends and How to Prepare Your Trading Edge
Data will increasingly separate winners from the rest. Traders who stitch together diverse signals, continuously validate them, and treat strategies as living systems will keep an edge when markets change. Expect on-chain transparency, alternative data sources, and faster automation to reshape what “alpha” looks like — but the advantage stays with disciplined testing and sensible risk controls.
Market data fusion and practical steps Data advantage: Combine traditional price/volume feeds with alternative sources such as order-book heat, news sentiment, or retail flow proxies to see moves earlier. Signal fusion: Merge on-chain metrics (when trading crypto) with off-chain macro and liquidity indicators to reduce false positives. * Real-time testing: Use short walk-forward windows and automated backtests to detect decay before it costs capital.
- Define a modular signal stack.
- Run controlled experiments where you add or remove a single input.
- Automate monitoring for performance drift.
that map to everyday trading Example — fusion alpha: A currency pair strategy that previously relied only on momentum improves entry precision by adding implied volatility skew and retail positioning; this cuts drawdown without changing the core edge. Example — Monte Carlo hardening: Running Monte Carlo simulations exposes tail behavior under different vol regimes, guiding position-sizing rules that survive sudden shocks. * Example — continuous deployment: A small systematic trader pushes weekly strategy updates with strict rollback rules; the iteration speed beats ad-hoc manual changes.
Practical tools and tactics Data hygiene: Maintain raw-data versioning and a reproducible pipeline so results are auditable. Signal validity checks: Track Sharpe-like metrics, hit rates, and time-to-first-loss for each signal component. * Risk overlays: Cap exposure by volatility-adjusted sizing and use stop-loss rules that match the strategy’s horizon.
Monte Carlo simulation for trading strategy enhancement: Use randomized returns and parameter sampling to estimate probable outcomes and inform sizing.
Long-term forex trading strategies for position traders: Focus on regime-aware entries and macro overlays to avoid whipsaw during structural shifts.
Expect continual adaptation to be the norm rather than the exception. Building the processes above turns uncertainty into manageable bets and keeps the trading edge viable through whatever comes next.
Quick Reference (Cheat Sheet)
Straight to the point: keep these formulas, checklists and emergency steps within reach. They’re geared for active traders who need fast, reliable rules to size positions, place stops, execute entries and de-risk when markets turn. Copy the position-sizing line into a notes app and print the checklist — they’re that practical.
Position sizing formula: Risk per trade (%) = Account size × Risk percentage per trade Position size (units) = (Account size × Risk%) / (Entry price − Stop price)
Example ready to copy: PositionSize = (AccountSize * RiskPercent) / (EntryPrice - StopPrice)
- When to use: sizing any trade where stop distance is known.
- Why it works: converts monetary risk tolerance into contract/shares size using actual stop distance.
ATR stop placement (average true range): Rule: Stop = Entry - (ATR × Multiplier) for longs; reverse for shorts. Typical multiplier: 1.5–3.0.
- When to use: volatile instruments or swing trades where price noise matters.
- Practical tip: use
ATR(14)on the timeframe you trade; higher multiplier for news or illiquid markets.
Top 5 execution checklist Clear thesis: Confirm technical pattern or fundamental catalyst aligns with trade idea. Order type chosen: Market vs limit vs stop; set limit for planned entries when liquidity is decent. Stops and targets set: Stop order placed immediately; targets sized so R:R ≥ 1.5 when possible. Slippage estimate: Add expected slippage (e.g., 0.1–0.5%) into worst-case sizing. * Liquidity check: Verify daily volume and spread match intended trade size.
- Review chart and confirm signal.
- Calculate position size using the formula above.
- Place entry as planned and set stop and profit orders.
- Monitor news and volume for execution risk.
- Adjust or cancel if market conditions change before fill.
Emergency de-risk steps Reduce size — close a portion (e.g., 25–50%) to cut exposure immediately. Tighten stops — move stop to break-even plus a small buffer to remove tail risk. Switch to hedge — buy a short-duration hedge (e.g., inverse ETF, option) if available. Pause new entries — stop initiating new trades until you reassess the setup.
Definitions
ATR: Average True Range, a volatility measure used to size stops and understand noise.
R:R: Reward-to-risk ratio; target distance divided by stop distance.
Slippage: Execution price difference between expected and actual fill.
Compact cheat sheet table summarizing formulas, checklists, and one-line rules for each strategy
| Item | Formula / Rule | When to use | Quick example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Position sizing | PositionSize = (AccountSize * Risk%) / (EntryPrice - StopPrice) |
Any trade with defined stop | Account ₦1,000,000, risk 1% → Risk₦10,000; Entry ₦800, Stop ₦760 → Size = 10,000/40 = 250 units |
| ATR stop placement | Stop = Entry - (ATR × Multiplier) (longs) |
Swing trades, volatile instruments | ATR(14)=15, Entry=500, Mult=2 → Stop=500−30=470 |
| Entry checklist | Use the Top 5 execution checklist above | Before placing order | Confirmed breakout + liquidity OK + stop set |
| Scaling rules | Add size on confirmation or trim on weakness; common split: 50/25/25 | Trend trades, partial profit-taking | Buy 50% at breakout, add 25% on retest, last 25% on momentum hold |
| Emergency exit | Reduce size → tighten stops → hedge → pause entries | When signals conflict or volatility spikes | Rapid gap down: close 50%, move stops to BE+, buy short hedge |
Key insight: this table turns the mental checklist into a rapid decision reference — use the position sizing line for every trade, rely on ATR for stop placement when markets are noisy, and keep the emergency steps memorized so reaction is fast rather than frantic.
Keep this sheet beside your platform. When the market speeds up, a short, practiced set of rules prevents emotional mistakes and preserves capital.
📥 Download: Cryptocurrency Trading Checklist (PDF)
FAQ
Below are the most common questions traders ask when building durable strategies for volatile Nigerian markets, with direct, actionable answers and suggested next steps.
What timeframe should I trade?
Shorter timeframes suit intraday traders who can monitor markets actively; longer timeframes reduce noise and favour position traders managing macro drivers. Choose a primary timeframe, then confirm signals on a higher timeframe to avoid false entries.
How much capital should I risk per trade?
Risking 1%–2% of equity per trade is a practical rule for most traders. Use position sizing to convert that risk into number of lots or units based on stop-loss distance.
- Calculate
risk per trade = account_size × risk_percentage. - Determine stop-loss in pips or price.
- Position size =
risk / (stop_loss × pip_value).
How do I protect against large drawdowns?
Diversify across uncorrelated instruments, use clearly defined stop-losses, and scale exposure down when volatility spikes. Monitor equity curve and cut strategies that consistently underperform.
What’s the simplest way to backtest a strategy?
Start with historical price data for the instrument, apply your rules on a spreadsheet or platform, and record entries, exits, and equity changes. Run through at least 200 trades or multiple market cycles before trusting results.
How can Monte Carlo simulation help my strategy?
Monte Carlo shows how returns vary under different trade orderings and streaks. Run simulations to estimate likely drawdown scenarios and to size the worst-case capital buffer. This is where statistical stress-testing turns optimism into realism.
Which indicators actually help in volatile markets?
- Volatility filters: help avoid entries during erratic moves.
- Trend-confirmation: prevents fading strong directional moves.
- Volume or liquidity checks: ensure trades can be executed without slippage.
When should I review or retire a strategy?
Review after a fixed number of trades or when performance deviates materially from expected metrics. Retire if edge disappears for a full market regime change or persistent negative expectancy appears.
Definitions
Drawdown: Peak-to-trough percentage loss of an equity curve.
Expectancy: Average return per trade after accounting for win-rate and pay-off ratio.
For deeper tools like Monte Carlo stress-testing or equity-curve analysis, consider running simulations against recent Nigerian market cycles and iterating rules until results match tolerance levels. That practical loop between testing and real-market experience is where robust strategies are built.
Resources and Further Reading
This collection points straight to tools, libraries and learning paths that traders in Nigeria can use immediately—grouped by purpose and with practical notes on accessibility and cost. Use the table for a quick scan and the bullets for action-oriented picks that match different experience levels and budgets.
Categorized list of recommended tools and resources with short descriptions and suggested user level
| Resource | Category | Best for | Notes (free/paid, region) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Binance | Exchange | Liquidity, spot & margin trading | Free signup, trading fees from 0.02%; wide NGN on/off ramps via P2P |
| Glassnode | On-chain analytics | Chain metrics, supply/flow analysis | Free tier; paid from $29/mo; global coverage, useful for BTC/ETH signals |
| Backtrader | Backtesting library | Strategy development, Python users | Open-source (free); local/backtest-focused; good for pandas workflows |
| CoinStats | Portfolio tracker | Multi-exchange portfolio aggregation | Free tier; Premium $4.99/mo; mobile-first, supports manual NGN entries |
| Coursera — Bitcoin and Cryptocurrency Technologies | Educational course | Foundational crypto theory | Audit free; paid certificate ~ $49; self-paced, academic depth |
Key insight: these five resources cover the essentials — execution, on-chain context, rigorous backtesting, portfolio oversight, and structured learning. Together they form a simple stack that scales from hobbyist to systematic trader.
Practical recommendations
- Start small: Use Binance P2P for easy NGN liquidity access before moving to advanced order types.
- Validate with data: Run new ideas in
Backtraderagainst at least 2 years of data before live sizing. - Monitor flows: Add an on-chain feed like Glassnode to spot macro shifts that conventional indicators miss.
- Track performance: Connect trades to CoinStats or a spreadsheet daily so slippage and fees are visible.
- Learn continuously: Pair a theoretical course with hands-on projects — e.g., replicate a published strategy then stress-test it with
Monte Carlopermutations.
For traders building robust plans in Nigeria, this list is practical and immediately actionable—pick one tool from each category and integrate it into a weekly routine to see clearer, faster learning gains.
Conclusion
Volatility will keep waking you at 3 a.m.; what changes is how you react. Keep your risk rules simple and consistent, automate routine checks where execution errors creep in, and treat backtests as living documents—not oracles. Remember the trader who combined position-sizing discipline with a tight stop framework and turned sporadic wins into a steady edge, and the quant who avoided slippage by routing orders through smarter execution. Those aren’t mysteries—they’re repeatable habits.
Move from theory to action with three concrete steps: define a maximum portfolio drawdown and enforce it, build one automated rule (position size or stop) into your platform, and run a focused backtest on that rule for at least six months of market data. If you’re asking “how big should my positions be?” err on the conservative side until the strategy proves itself in live conditions; if you wonder about taxes and record-keeping, start a dedicated ledger now. For practical templates, see the Resources and Further Reading section on NairaFX for checklists and execution playbooks.
Take one small change this week—implement a stop framework or run a fresh backtest—and treat the result as data. That single disciplined iteration compounds faster than any overnight swing.

